When it comes to the construction or upkeep of high-performance PCs, one thing many overlook that is also important is thermal paste. This study of thermal paste will begin to unpack how this small tube of thermal compound contributes to CPU cooling, heat transference, and temperature management to keep your system operating at maximum efficiency. Whether you are building a PC for the first time or are an enthusiast trying to get every ounce of performance out of your system, knowledge of thermal paste and how to use and care for it will go a long way.
Thermal paste (also colloquially known as thermal compound or thermal grease) is designed to actually do one thing: fill microscopic air pockets between your CPU and the baseplate of your cooler. Left unfilled, these air pockets become insulators and trap heat, which is something every system builder is trying to avoid.
The purpose of any CPU cooling system is straightforward: to transport heat from the CPU to the heatsink and then to nearby air effectively. Even with the best metals in the world, they are not smooth—there are microscopic defects. Thermal paste allows effective heat transfer while maintaining effective temperature regulation in instances where the CPU reaches maximum temperature.
If you don't have the right thermal paste, even the most expensive cooler won't work well. Plus, improper application can lead to drastic spikes in temperature, throttling, heat changes, and even catastrophic permanent CPU failures. This thermal paste how-to guide will help you pay the right attention to get the most out of your cooling.
There are several types of thermal paste. Each is designed for single performance-maintenance purposes. They meet specific needs and price points.
Metal-based pastes generally include micronized metal particles and have a good thermal transfer performance. They are best for enthusiasts who want to overclock or maintain temperatures tightly controlled, even with heavy workloads. However, since they are also electrically conductive, you have to be precise with the application to avoid any possibility of short-circuiting.
Ceramic compounds are non-conductive and easy to use. Ceramic compounds may not match the performance of metal compounds as a CPU cooling option, but they are a viable option for casual and non-competitive users, particularly for general maintenance, due to their safety and durability.
Carbon-based compounds are designed for safety and performance—they provide excellent heat transfer while remaining non-conductive, making them great for gamers, streaming and content creators, or anyone searching for a thermal compound that will get the job done.
Liquid metal compounds, which are mainly made of gallium alloys, provide the highest cooling performance. However, these compounds are difficult to apply and extremely conductive-perfect only for experienced users who understand the ins and outs of application tips and the dangers involved.
A flawless thermal paste application can make or break your CPU cooling setup. Using too much paste causes a messy application and poor thermal control of the CPU and cooler, while using too little paste will not provide enough coverage of the surface area to ensure effective heat transfer.
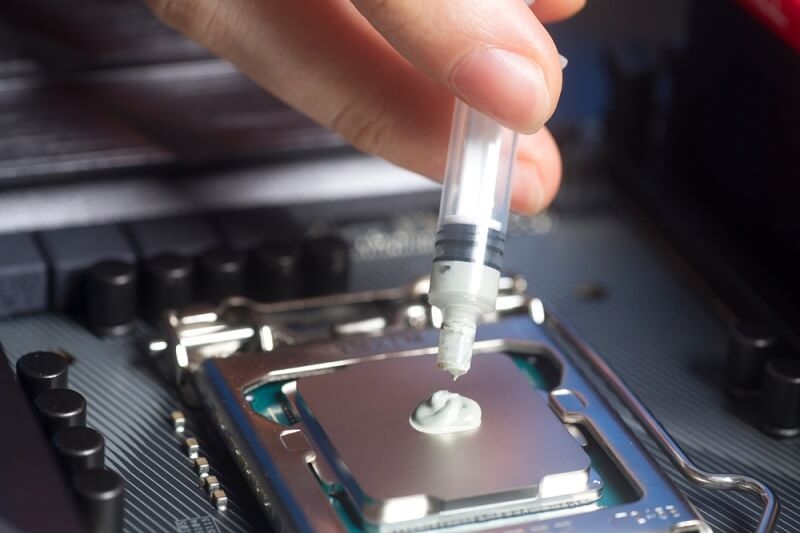

Always clean the old thermal paste and residue from the CPU and cooler base with isopropyl alcohol on a lint-free towel before applying a new thermal paste. Cleaning the CPU and cooler will ensure a smooth interface to facilitate heat transfer.
A pea-sized drop of thermal paste in the center of your CPU is usually plenty. When you mount the heatsink, pressure spreads the paste out evenly across the chip. For larger CPUs, like AMD Threadripper, a small X-pattern may work better.
Using an excessive amount of thermal paste can actually be detrimental to temperature regulation. Any paste that spills out can make an insulating layer that prevents heat from transferring efficiently and can affect overall performance management.
When fastening the heatsink down, apply even pressure in every corner to contribute to an even thermal paste layer. If the heatsink isn’t evenly mounted, it can create air pockets, which deteriorate overall CPU cooling performance.
After you have installed your CPU back into your system, be sure to track temperatures with software such as HWMonitor or Core Temp. When values are higher than expected, it is a direct correlation to either poor thermal paste application or issues with heatsink contact.
The CPU serves as the brain of your PC, so when it is processing, it produces heat continuously. Quality thermal paste allows heat to transfer from the CPU efficiently to the cooler. If you don't manage the temperature effectively, the performance of the computer will be curtailed through thermal throttling in order to prevent heat damage.
Used as a heat sink, the thermal paste is discounted because a few degrees in temperature management can be critical, not only for thermal management but also for overall performance and CPU lifespan under heavy, extended loads.
Like any other component of your computer, thermal paste will expire. Eventually, it will dry, crack, or otherwise lose effectiveness in heat transfer. Proper maintenance of performance is temperature management, checking, and replacing the thermal paste as needed.
If any of these occur, it’s time for a refresh. Thoroughly clean all of the old thermal paste off prior to following the instructions above to apply new thermal paste.
Every two to three years is sufficient for most users, but enthusiasts who routinely swap out computer components or put their systems through stress tests should consider annual replacement for optimal CPU cooling.
Never store unused thermal paste in hot, humid conditions.
Ignoring this could contaminate it due to air or heat exposure, reducing quality during further applications.
Even seasoned builders occasionally make mistakes that negatively impact temperature control. Some types of thermal paste you will want to avoid:
Avoiding these pitfalls ensures your thermal paste delivers maximum efficiency.
The choice of a thermal paste depends on the purpose of your PC. Everyday users have a safe enough option in non-conductive ceramic or carbon-based alternatives that provide good CPU cooling. High-performance metal-based or liquid-metal compounds would provide the best results in heat transfer and perfect temperature control for gamers, creators, and overclockers.
Before buying your thermal paste, check the thermal conductivity rating (denoted in W/mK). Higher values will transfer heat better - and that’s what you want for maintaining a thermal efficiency under load during performance maintenance.
Face it, you are going to want a stable and cool machine for a few years of development.
The more of these easy habits you can develop, the longer you can keep your CPU functioning and your desktop running like it did the day it was first turned on.
A small amount of thermal paste can make a significant difference in CPU cooling, thermal transfer, and temperature management. As we have demonstrated in the thermal paste guide, it is the skill you develop with application and the knowledge of its management that will take your performance and reliability to whole new levels.
So whether you are building a new rig, upgrading your cooler, or simply keeping up with your upkeep, never underestimate the abilities of the proper thermal paste application. Thermally pasting is the unseen hero of every computer that operates seamlessly and reliably while also keeping everything cool, efficient, and sustainable in the long term.
This content was created by AI